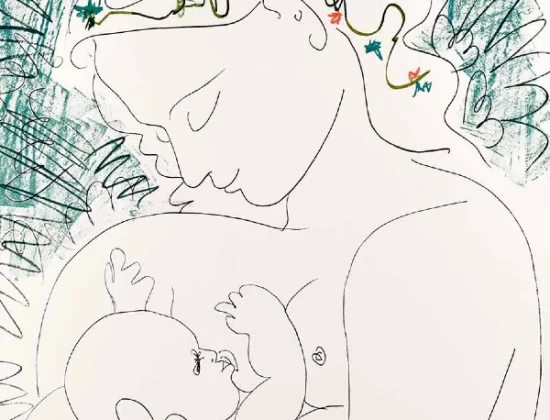
“Yet Cubism and Modern art weren’t either scientific or intellectual; they were visual and came from the eye and mind of one of the greatest geniuses in art history.”
As one of the most influential Modern artists of the 20th century, Pablo Picasso is renowned as a legendary artistic master to this day. Born on October 25, 1881 in Malaga, Spain, Pablo Picasso was a child prodigy who was recognized as such by his art-teacher father, who ably led him along. The small Museo de Picasso in Barcelona is devoted primarily to his early works, which include strikingly realistic renderings of casts of ancient sculpture.
Picasso was a rebel from the start and, as a teenager, began to frequent the Barcelona cafes where intellectuals gathered. He soon went to Paris, the capital of art, and soaked up the works of Edouard Manet, Gustave Courbet, and Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, whose sketchy style impressed him greatly. Then it was back to Spain, a return to France, and again back to Spain – all in the years 1899 to 1904.
Before he struck upon Cubism, Picasso's artwork went through a prodigious number of styles – realism, caricature, the Blue Period, and the Rose Period. These distinguished styles are apparent in the unique original works as well as Picasso ceramics, lithographs, linocuts, and etchings that he created later in his life.
The Blue Period dates from 1901 to 1904 and is characterized by a predominantly blue palette and focuses on outcasts, beggars, and prostitutes. This was when he also produced his first sculptures. The most poignant work of the style, La Vie (1903), currently located in Cleveland’s Museum of Art, was created in memory of his childhood friend, the Spanish poet Carlos Casagemas, who had committed suicide. The painting started as a self-portrait, but Picasso’s features became those of his lost friend. The composition is stilted, the space compressed, the gestures stiff, and the tones predominantly blue.
The Rose Period began around 1904 when Picasso’s palette brightened and is dominated by pinks and beiges, light blues, and roses. His subjects are saltimbanques (circus people), harlequins, and clowns, all of whom seem to be mute and strangely inactive. One of the premier works of this period is Family of Saltimbanques (1905), currently in Washington, D.C. at the National Gallery, which portrays a group of circus workers who appear alienated and incapable of communicating with each other, set in a one-dimensional space.
In 1905, Picasso went briefly to Holland, and on his return to Paris, his works took on a classical aura with large male and female figures seen frontally or in distinct profile, as in early Greek art. One of the best examples of this style is in the Albright-Knox Gallery in Buffalo, NY, La Toilette (1906). Several pieces in this new, classical style were purchased by Gertrude Stein (the art patron and writer) and her brother, Leo Stein.
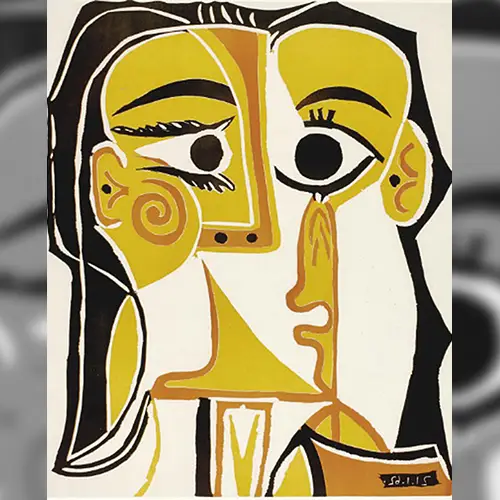
With his groundbreaking 1907 painting Les Demoiselles d’Avignon, Picasso, along with Georges Braque, developed a revolutionary style of modern art that was formed in response to the rapidly changing modern world: Cubism. He simplified and distorted figures and objects into geometric planes, often including elements of text and collage in his works.
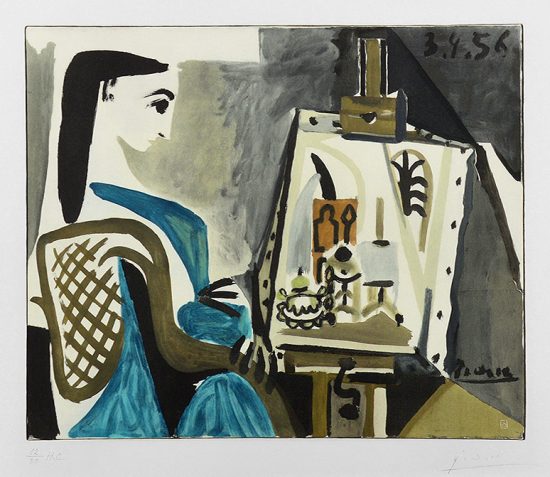
Picasso enjoyed creating his art in many different artistic mediums throughout his life and, in due time, became a master in each medium. From Picasso ceramics to paintings to lithographs, etchings, and linocuts, all of his works are a testament to his artistic skills. There are even hand signed Picasso prints that are worth more than unique original works.
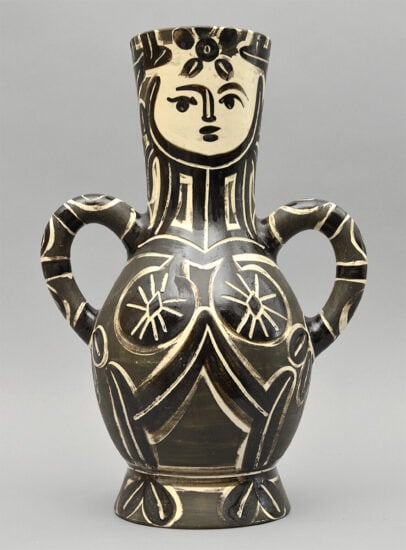
Pablo Picasso Ceramics
Pablo Picasso's foray into ceramics stands as a remarkable testament to his artistic versatility and boundary-pushing creativity. Renowned primarily as a painter and sculptor, Picasso's exploration of ceramics added a new dimension to his already groundbreaking career. In the late 1940s, he turned his attention to the medium, collaborating with skilled potters in the South of France. What emerged was a stunning array of ceramic pieces that reflected Picasso's distinctive style and innovative spirit.
With a keen eye for abstraction and a penchant for reimagining forms, Picasso's ceramic works exude an unmatched sense of playfulness and experimentation. His designs often incorporated whimsical creatures, human figures, and abstract shapes, each one capturing the essence of his artistic vision. The tactile nature of ceramics allowed Picasso to infuse his works with a tangible and intimate quality, inviting viewers to engage not only visually but also through touch.
Picasso's ceramics demonstrate a fusion of tradition and modernity, as he drew inspiration from both ancient pottery techniques and contemporary art movements. This unique amalgamation resulted in pieces that are simultaneously timeless and daringly innovative. From charming plates adorned with joyful scenes to intricately sculpted vases that seem to defy gravity, Picasso's ceramics push the boundaries of what clay can achieve.
Moreover, these ceramic works offer a glimpse into Picasso's personal life and mindset. They unveil his fondness for the Mediterranean lifestyle, evident in the vibrant color palette and lively imagery he employed. The ceramics also reflect his capacity for reinvention, showcasing his ability to adapt to new mediums while leaving an indelible mark.
Today, Picasso's ceramics are revered as integral components of his oeuvre, celebrated in museums and private collections around the world. They serve as a reminder that true artistic genius knows no limitations, and that even a master of one domain can find fresh inspiration and mastery in another. Picasso's ceramics continue to inspire artists and enthusiasts alike, a testament to his enduring influence on the ever-evolving landscape of art.